Hibernation is one of the power-saving modes offered by Windows. This feature is very useful if you want to turn off your computer without losing all your open documents, browsers, programs, and current settings. So the next time your computer starts up, you can resume working from where you left off.
However, hibernation has some downsides. The shutdown takes longer
because all your open files and settings from the RAM will be written
to a file on your hard disk. This file is called hiberfil.sys, which
is roughly the size of your RAM. This means that if you have 2GB of
RAM, your hiberfil.sys file is something close to 2GB. Now, that's
perfectly fine if you do use hibernation. But if you don't, then this
file is just a waste of space. You can free up this extra space by
disabling hibernation. Here is how:
- Make sure you are logged in as administrator
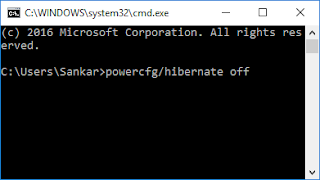
- Click on the Start button and type cmd in the Search box (XP users will need to click on Start - Run and type cmd). Hit Enter. This will open the Command Line
If at any time you'd like to re-enable hibernation, simply repeat
steps 1-4, but type powercfg /hibernate on in step 3 instead.
No comments:
Post a Comment